⏱️ 4 min read
Did You Know? 10 Fun Facts About Quantum Physics
Quantum physics, the study of matter and energy at the smallest scales, is filled with mind-bending concepts that challenge our everyday understanding of reality. Here are ten fascinating facts about quantum physics that showcase just how strange and wonderful our universe truly is.
1. Quantum Tunneling Makes Life Possible
Quantum tunneling allows particles to pass through barriers that classical physics says they shouldn’t be able to cross. This phenomenon makes nuclear fusion possible in the Sun’s core, where particles tunnel through the intense electromagnetic repulsion to fuse together. Without quantum tunneling, stars wouldn’t shine, and life as we know it wouldn’t exist. It’s also the same principle that enables modern technologies like scanning tunneling microscopes.
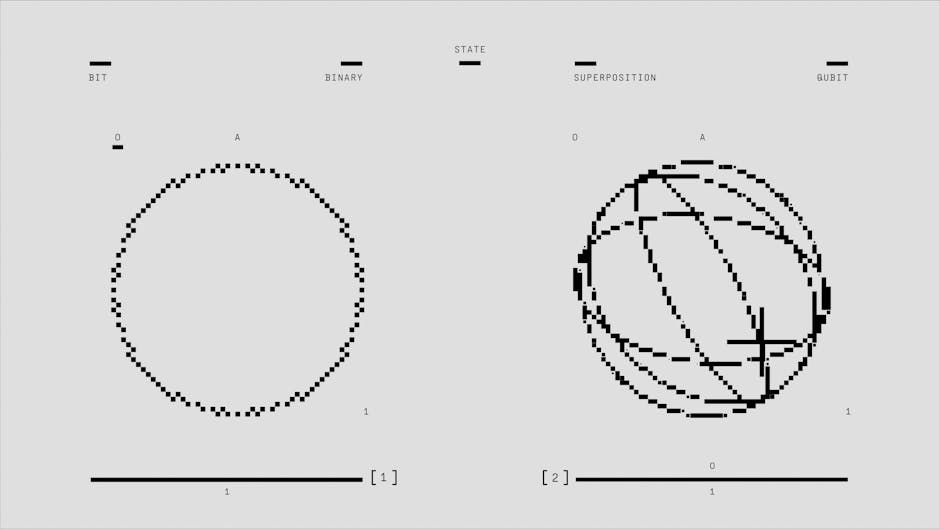
2. Particles Can Be in Multiple Places at Once
According to quantum superposition, particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously until they are observed or measured. This isn’t just theoretical – scientists have demonstrated this phenomenon with particles as large as molecules containing hundreds of atoms. The famous “double-slit experiment” demonstrates this principle, showing how particles can travel through two slits simultaneously as waves until they are observed.
3. Quantum Entanglement Defies Space and Time
Einstein called it “spooky action at a distance” – when two particles become entangled, their quantum states are linked regardless of how far apart they are. Changes to one particle instantaneously affect the other, seemingly violating the speed of light limitation. This principle is now being used to develop quantum computers and secure communication systems.
4. The Observer Effect Changes Reality
In quantum physics, the mere act of observing a particle can change its behavior. This isn’t because of physical interference from measuring instruments, but rather because observation itself forces the particle to “choose” a definite state from its many possible states. This principle fundamentally challenges our understanding of objective reality.
5. Quantum Levitation Is Real
Through a phenomenon called the Meissner effect, scientists can make objects levitate using quantum physics. When certain materials are cooled to extremely low temperatures, they become superconductors and expel magnetic fields, allowing them to float above magnets. This principle has practical applications in magnetic levitation trains and advanced medical imaging equipment.
6. Time Can Flow Backwards
At the quantum level, time becomes more flexible than we normally experience it. Some quantum phenomena appear to work the same whether time moves forward or backward, and certain experiments have shown particles can influence their own past states. This quantum time symmetry challenges our macroscopic understanding of cause and effect.
7. Quantum Computers Can Solve “Impossible” Problems
Unlike classical computers that use bits (0 or 1), quantum computers use quantum bits or “qubits” that can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This allows them to perform certain calculations exponentially faster than classical computers, potentially revolutionizing fields like cryptography, drug discovery, and climate modeling.
8. The Quantum Zeno Effect Freezes Time
Named after the ancient Greek philosopher Zeno, this effect shows that an unstable particle will never decay while it is being continuously observed. It’s as if time stops for the particle under constant measurement. This has been demonstrated in laboratories and has potential applications in quantum computing and precision measurements.
9. Vacuum Is Not Empty
Quantum mechanics reveals that even perfect vacuum contains fluctuating electromagnetic fields and virtual particles that pop in and out of existence. These quantum fluctuations contribute to what physicists call “vacuum energy” or “zero-point energy,” and they may have played a crucial role in the early universe’s expansion.
10. Quantum Biology Exists in Nature
Recent discoveries show that quantum effects play important roles in biological processes. For example, photosynthesis relies on quantum coherence to achieve its remarkable efficiency, and some scientists believe birds use quantum entanglement in their magnetic navigation systems. Even our sense of smell might depend on quantum mechanics.
Conclusion
These ten quantum physics facts demonstrate how the microscopic world operates under rules that seem to defy our common-sense understanding of reality. From enabling the Sun’s power to potentially revolutionizing computing and showing how biology harnesses quantum effects, quantum physics continues to reveal new wonders about our universe. As research advances, we may discover even more remarkable ways that quantum phenomena influence our world and shape our future technologies.
Understanding these quantum principles not only helps us appreciate the fascinating complexity of nature but also drives innovations in technology, medicine, and our understanding of life itself. While quantum physics may seem abstract, its applications and implications touch every aspect of our modern world.